Live Chat
Domain Scan

(empty)

Login
Database Guide: How to Create and Insert Data to a Database
(25-jun-2025)

Every modern website relies on a database-it's the silent engine that stores everything from user details and form submissions to product listings and blog content. Whether you're running a small portfolio or a growing online platform, having a database working in the background ensures your data is organized, accessible, and secure. With the right tools, you can take control of your website's data and unlock features that make your site smarter, faster, and more dynamic.
How Databases Can Power Your Website - and Why It Matters
Databases form the backbone of any dynamic website or online application. Whether you're building a contact form, managing product listings, tracking orders, or storing newsletter signups, a database lets you organize, store, and retrieve data in real time. By connecting your website to a database through backend programming (like PHP, Node.js, or Python), you can make your content interactive and data-driven.
You're not limited to one type of data. You can create multiple databases-one for customer information, another for orders, another for blog posts, and so on. Each can have its own tables and structure based on your specific needs.
Why Use Databases on Your Website?
- Dynamic Functionality: Display personalized or changing content without editing static pages.
- Scalability: Handle thousands of entries or users with ease.
- Data Control: Add, update, or delete records anytime through SQL or your app's backend.
- Separation of Logic and Design: Keep your data and interface separate, which simplifies maintenance.
- Enhanced Features: Enable search, login systems, dashboards, and reporting tools seamlessly.
Whether you're building a portfolio site, an eCommerce platform, or a custom web application, a well-structured database will give you the power to grow and adapt your project efficiently.
In this step-by-step guide, we'll walk you through how to set up your own database, create a table to store customer information, and insert and view that data using both the phpMyAdmin interface and SQL queries. Let's dive in and bring your data to life!
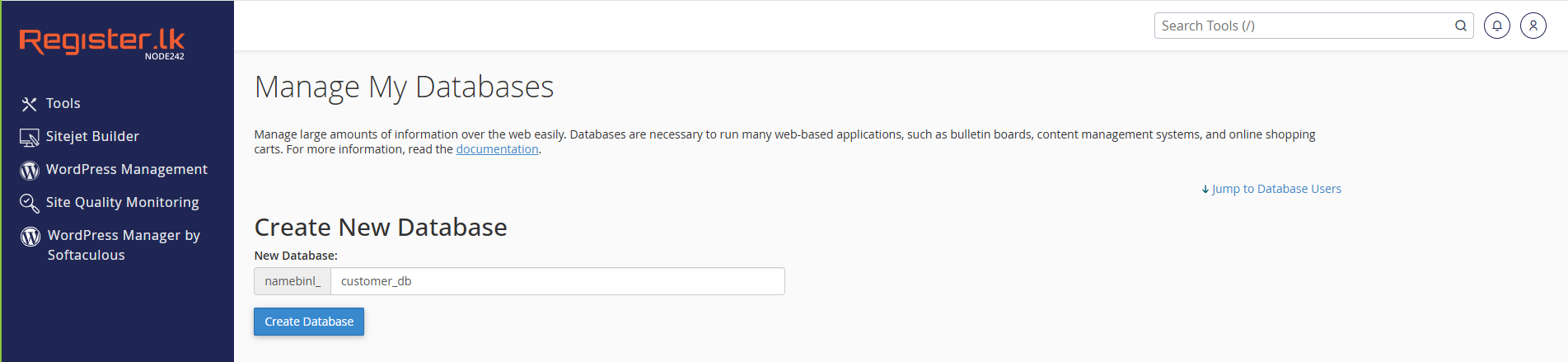
Step 1: Create a New Database from cPanel
- Log in to cPanel
Access your cPanel at
yourdomain.com/cpanelwith your hosting credentials. - Scroll down to the Databases section.
- Click on Manage My Databases.
- Under Create New Database, enter a name like
customer_db. - Click Create Database.
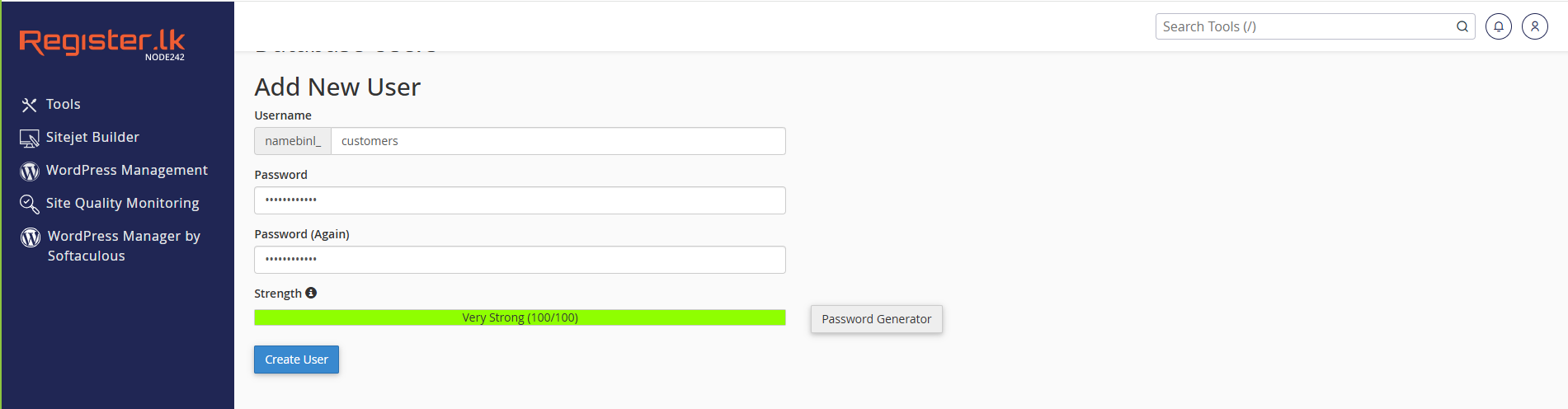
Once created, scroll down to add a new user:
- Enter a Username and Password under "MySQL Users."
- Click Create User.
Then assign the user to the database:
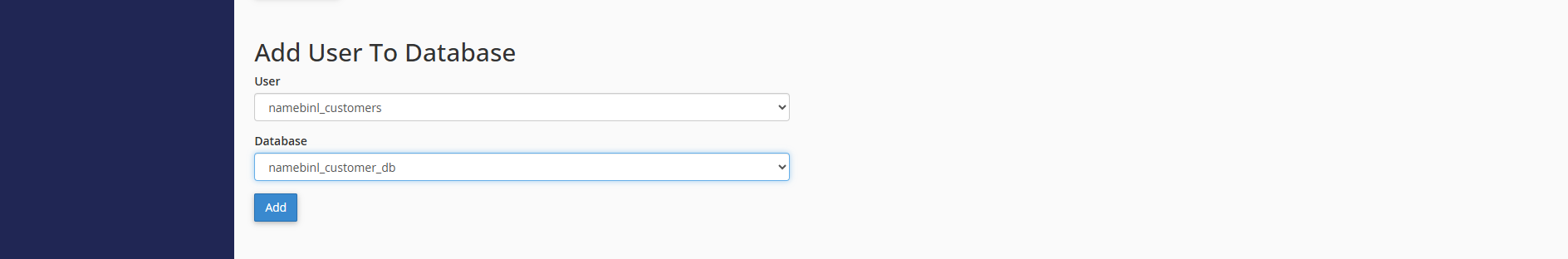
- Under Add User to Database, choose the newly created user and database.
- Click Add, then select All Privileges, and click Make Changes.
Step 2: Access phpMyAdmin
- Go back to the main cPanel dashboard.
- Click on phpMyAdmin under the Databases section.
- In phpMyAdmin, select the newly created database (customer_db) from the left sidebar.
Step 3: Create a Table in the Database
Method 1: Using phpMyAdmin Interface
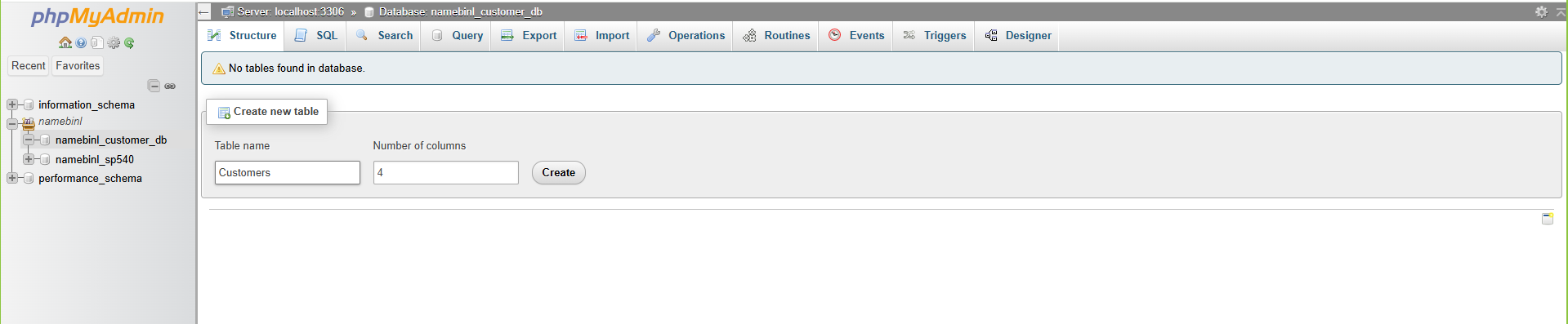
- In the selected database, find the Create table section.
- Enter table name: Customers
- Set number of columns: 4
- Click Create
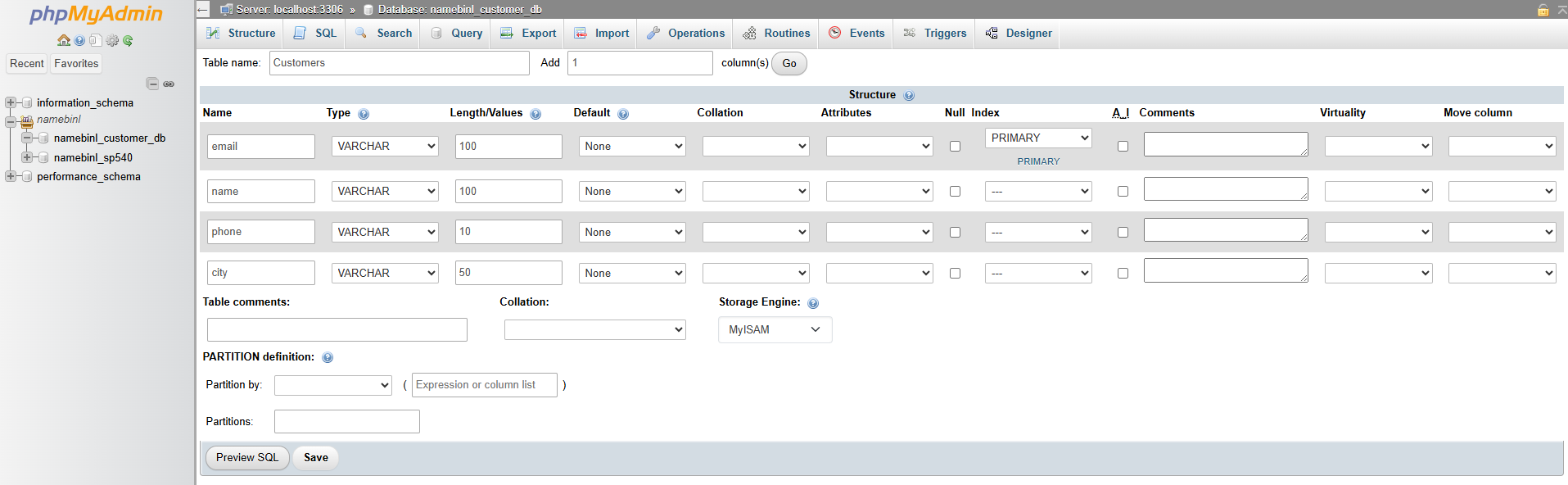
- Configure the fields:
Method 2: Using SQL Query in phpMyAdmin
Click on the SQL tab and run:
CREATE TABLE customers (
email VARCHAR(100) PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
phone VARCHAR(15),
city VARCHAR(50)
);
Feel free to modify the number of fields, field names, data types, and lengths based on the kind of data you intend to store.
Step 4: Insert Data into the Table
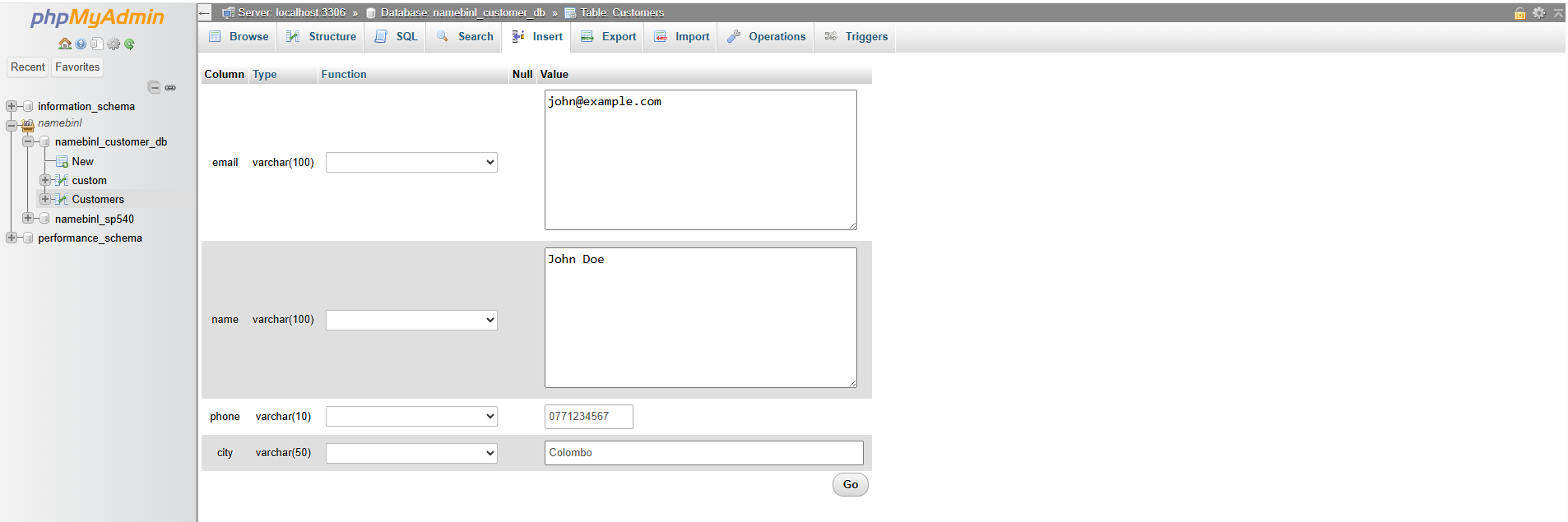
Method 1: Using phpMyAdmin Interface
- Click the customers table from the left panel.
- Open the Insert tab.
- Fill in sample customer details:
- email: john@example.com
- name: John Doe
- phone: 0771234567
- city: Colombo
- Click Go to save the entry.
Method 2: Using SQL Query
Navigate to the SQL tab and run:
INSERT INTO customers (email, name, phone, city)
VALUES ('john@example.com', 'John Doe', '0771234567', 'Colombo');
You can use SQL queries in your website's backend code to insert, update, or delete data in your database tables.
Step 5: View the Stored Data
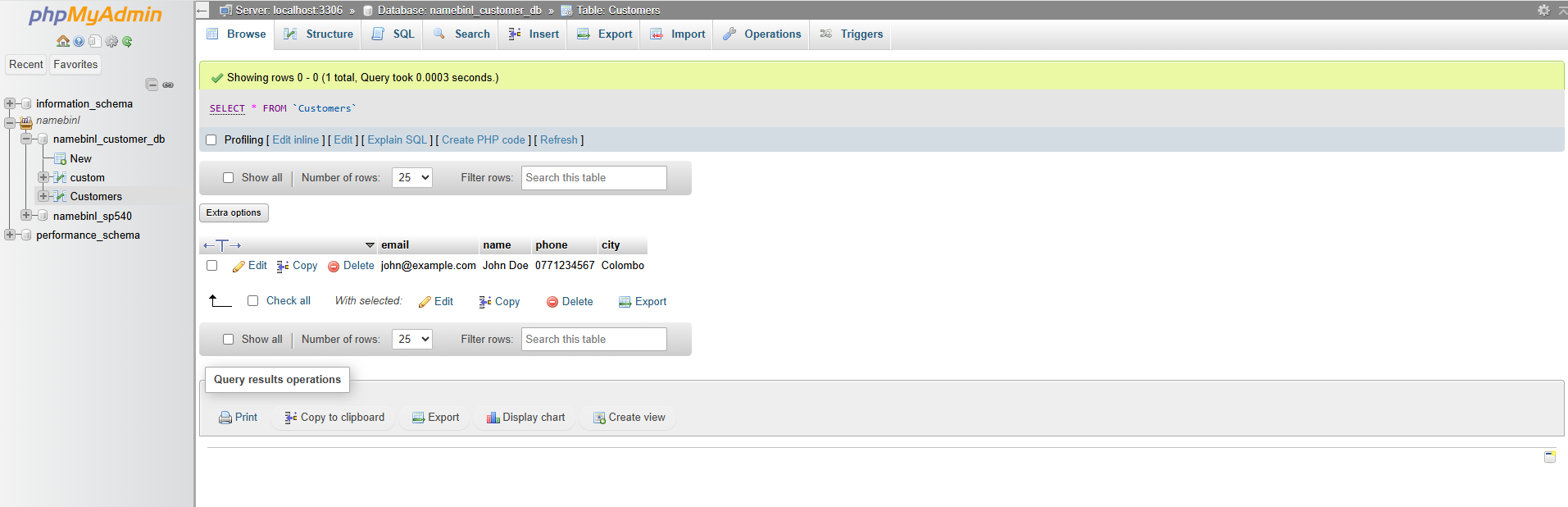
Method 1: Using phpMyAdmin Interface
- Click the Browse tab on the top menu.
- Your saved customer records will appear in a table format.
Method 2: Using SQL Query
To fetch all records, run:
SELECT * FROM customers;
Your database is now fully set up-you've created it, added a table, inserted data, and viewed it successfully.
Conclusion
Setting up a database might seem technical at first, but with cPanel and phpMyAdmin, the process becomes simple and accessible-even for beginners. Whether you're managing customer details, handling product records, or preparing for future website features, having a structured database is essential. By learning to create tables, insert data, and run SQL queries, you're taking a solid step toward building more powerful, dynamic websites. Keep exploring, and let your data work for you!
Start building your database today and organize your data like a pro!
 Written by: Register.lk Support Hero - Yusuf
Written by: Register.lk Support Hero - Yusuf